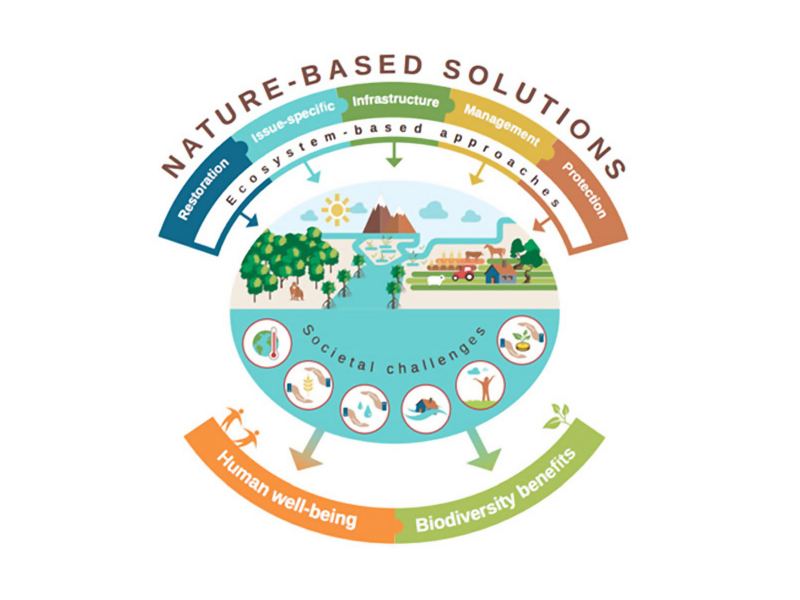
Nature-based Solutions (NbS) that enhance climate resilience are pragmatic solutions building on the services and resources provided by ecosystems and biodiversity, which are more sustainable, robust and often more cost-efficient than conventional man-made solutions alone.
Here are the main findings and key policy recommendations from the policy paper "Outsmart climate change: work with nature! Enhancing the Mediterranean’s climate resilience through Nature-based Solution."
MAIN FUNDINGS
1. The Mediterranean region has been identified as a climate change ‘hotspot'. Average temperatures in the region have already risen to 1.6°C above pre-industrial levels, while a temperature rise of 2-3°C by 2050, and a rise of 3-5°C by 2100, have been forecast for the region (IPCC, 2013). This will lead to an increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as droughts, heat waves, storms and floods.
2. Conventional infrastructure alone will not be able to cope with this new, highly dynamic and challenging context, which implies a significant level of uncertainty. Robust but flexible solutions are needed to help societies adapt.
3. Biodiversity and healthy ecosystems provide a broad range of services – through Nature-based Solutions (NbS) – in terms of adaptation to and mitigation of climate change and can increase society’s overall resilience to stresses and shocks (FAO, 2019).
4. NbS are generally robust, flexible, cost-efficient, inclusive and long-term oriented solutions. Stand alone or combined with man-made solutions, they also offer co-benefits related to food security, livelihoods, improved health and well-being, water regulation and disaster risk reduction, while contributing to nature conservation and restoration.
5. To facilitate the deployment and implementation of NbS and fully reap their benefits, shifts in mindsets, public policies (including legal and regulatory frameworks), and sound investment opportunities are needed. This will help to overcome current barriers and allow NbS to reach their maximum potential.
KEY POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS
1. Within the framework of the Barcelona Convention, develop a strategy to fully integrate NbS into national policies across all sectors so as to significantly enhance countries’ climate resilience by 2030.
2. In particular, mainstream NbS into national plans for climate mitigation and adaptation, such as the NDCs (Nationally Determined Contributions) and NAPs (National Adaptation Plans) required under the Paris Agreement, and DRR (Disaster Risk Reduction) plans under the Sendai Framework.
3. Foster “Green City” schemes throughout the region to improve citizens’ resilience to heat waves, flood surges and coastal erosion, and possible water and food shortages.
4. Promote sustainable and biodiversity-friendly practices and initiatives in the field of agriculture and aquaculture, such as agroecology, local integrated nature-based production systems and sustainable fisheries to secure food security, rural and coastal livelihoods and employment opportunities.
5. Manage coastal and marine ecosystems, including wetlands, in a sustainable manner to enhance their capacity as carbon sinks and buffers, restore depleted fish stocks and protect marine biodiversity.
6. Overall, implement adequate institutional structures, economic incentives and land tenure instruments to facilitate the uptake and implementation of NbS and overcome existing obstacles to their implementation with a view to moving towards a blue-green and circular economy and ensure society’s long-term resilience.
Read the full policy paper here.